How Oncology Surgeons Collaborate with Other Cancer Specialists
Oncology surgery has a most important role in the treatment of cancers, but it is part of an overall approach toward the care of cancer. Therefore, there is big collaboration between the oncology surgeons and other specialists to do with cancer care, such as medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, and supportive care teams in order to deliver holistic and effective treatments to patients. Such collaboration ensures that everything pertaining to a patient's care is well thought out and executed to achieve its ultimate objective: improvement in the quality of life for the patients.
The Role of Oncology Surgeons
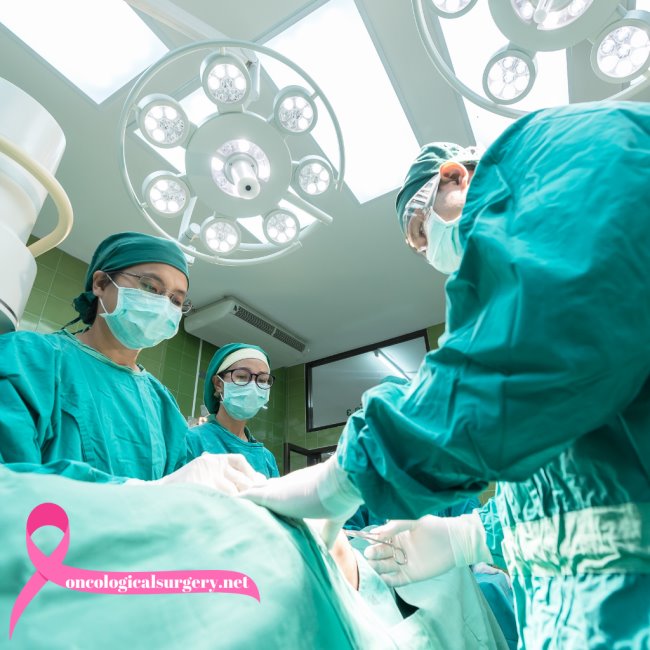
Oncology surgeons are the masters of surgery techniques for tumor and cancerous tissue removal. Their input is important in the management of various cancers like Colon Cancer Treatment, Pancreatic Cancer Treatment, Stomach Cancer Treatment, and Thyroid Cancer Treatment. Oncology surgeons usually play a critical role in the diagnosis, staging, and initial removal of tumors, which helps other specialists make a proper treatment plan.
Collaboration with Medical Oncologists
Medical oncologists are specialists who deal with the non-surgical management of malignancies, mainly employing chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy. Several areas make the collaboration between oncology surgery and medical oncologists important, including the following:
- Preoperative Treatment: Medical oncologists may give neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery in order to diminish the size of a tumor. This makes surgical removal easier and less invasive.
- Postoperative Care: After surgery, the medical oncologist may recommend adjuvant chemotherapy to kill the remaining cancerous cells, preventing disease recurrence.
- Follow-up Care Continuously: The medical oncologists keep the patients' conditions monitored for the continuation or recurrence that may arise, besides managing the long-term treatment plans to ensure smooth transition of the patients from surgical towards medical management.
Referring Radiation Oncologists
- Radiation oncologists specialize in using radiation therapy to treat cancer. Their work, in coordination with the oncologic surgeons, forms an important part of the treatment plan for the following reasons.
- Preoperative Radiation: As in chemotherapy, radiation therapy can also be applied before surgery in order to minimize tumor size and optimize surgical outcome.
- Intraoperative Radiation: Sometimes, radiation is administered right at the time of surgery by intraoperative radiation therapy in order to increase the exacting accuracy against the cancer cells.
- Radiation after Surgery: The aim of postoperative radiation is to destroy the lingering cancer cells that may be lingering around and those cancers that have a propensity for local recurrence.
Collaboration with Pathologists
- The pathologist's contribution to diagnosing and determining the kind and stage of cancer is an invaluable one. Medical and radiation oncologists also rely on the services of pathologists in providing an accurate diagnosis and staging on which treatment plans are directly based:
- Analysis of Biopsy Specimen: The pathologists analyze biopsy specimens derived during surgery to identify the presence and nature of the tumor.
- Margin Testing: After surgical resection of a tumor, the surgical margins are examined by pathologists to see whether the tumor has been completely removed.
- Molecular Testing: Tumor tissues are assessed for mutations by pathologists at molecular and genetic levels. Their presence will recommend targeted therapy.
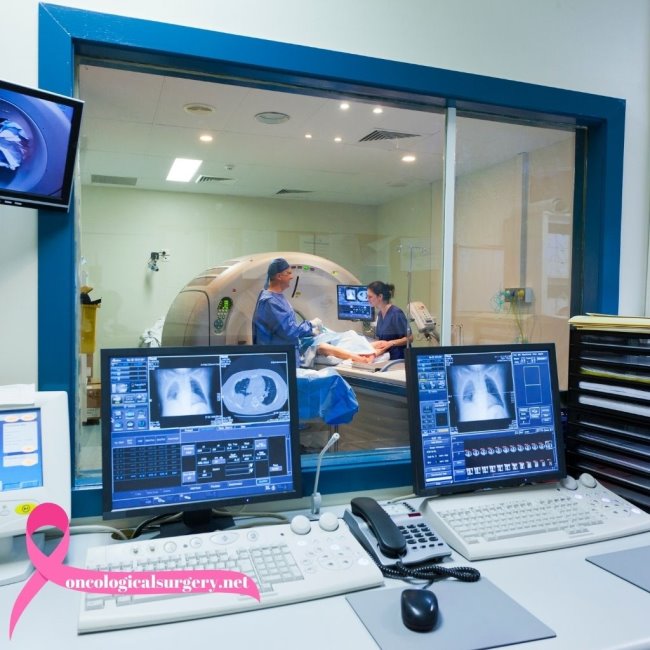
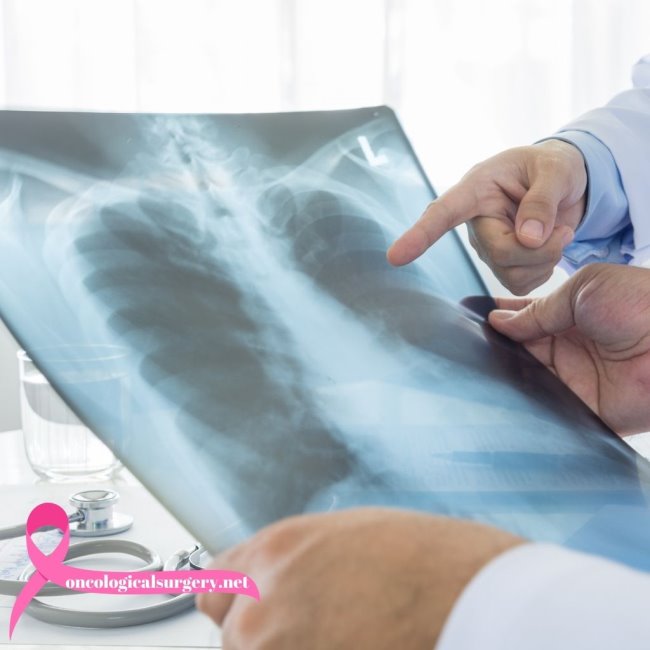
Collaboration with Radiologists
- Radiologists also play a significant role in the imaging and diagnosis of malignancies. The oncology surgeons collaborate with the radiologists in getting the finer details for proper surgical planning and also assess the post-operation conditions of the patients:
- Diagnostic Imaging: Radiologists perform and interpret imaging studies, including CT scans, MRI, and PET scans, among others, in order to localize tumors and estimate the size and extent of spread.
- Surgical Planning: Such detailed imagery can help the oncology surgeon in planning the most appropriate surgical intervention and thereby limit injury to surrounding tissues.
- Postoperative Care: After the surgery, the radiologist provides follow-up imaging to monitor for recurrence of the disease and the overall success of the surgical procedure.
Collaboration with Supportive Care Teams
The supportive care teams consist of services from various personnel, including a palliative care specialist, nutritionist, physical therapist, and mental health professional. They provide comprehensive management to the cancer patient. The interaction and cooperation with an oncology surgeon are very crucial for the following reasons:
- Pain Management: Symptom and pain management by a palliative care specialist improve the quality life of a patient during and after treatment.
- Nutritional Support: The nutritionist provides dietary plans to help the patient regain his strength and health, generally helpful during post-treatment recovery.
- Rehabilitation: Physiotherapists help in the rehabilitation of the patient by helping them regain their lost strength and mobility following surgery.
- Mental Health Support: Psycho-oncologists provides psychotherapy as well as support to the patient and his relatives regarding the psychological aspects of cancer treatment
- Case Study: Interdisciplinary Approach in Management of Pancreatic Cancer
To comprehensively understand why teamwork forms an integral part of oncology surgery, one has to revert to a case study of a patient undergoing treatment for pancreatic cancer :
- Diagnosis: The patient undergoes the initial diagnosis, which includes imaging and biopsy. Radiologists together with pathologists confirm the presence of cancer and the stage.
- Treatment Planning: The oncology surgeon consults medical and radiation oncologists on a treatment plan. The patient is given neoadjuvant chemotherapy as a way of shrinking the tumor before surgery.
- Surgical Interventions: The surgical intervention by the oncology surgeon is highly complex to remove the tumor. During the said surgery, the pathologist examines the excised tissue to make sure that clear margins are obtained.
- Postoperative Care: The patient is given adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy post-surgery to kill the remaining cancerous cells. The supportive care team administers pain management, nutritional support, and rehabilitation services.
- Follow-up Care: Ongoing follow-up care with the oncologic surgeon, medical oncologist, and radiologist confirms that the patient remains disease-free. Supportive care addresses long-term effects of the treatments.
Challenges and Future Directions
While collaboration among cancer specialists is paramount, it also can be difficult. Coordinating care across multiple disciplines requires effective communication and a shared commitment to patient-centered care. Advances in technology and the development of multidisciplinary cancer centers have made collaboration easier, but ongoing efforts are necessary to make processes smoother and improve results.
Looking to the future, AI and machine learning hold great promise in integrating cancer care. AI will interpret big data on complex treatment responses and provide personalized care planning that will enhance efficiency and effectiveness in the management of cancer.
Conclusion
This would be the essence of collaboration in the chain of oncology surgeons along with other specialists responsible for complete and efficient care in cancer. Such collaboration allows these professionals to make out that the best, appropriate, and personalized treatment is being delivered right from diagnosis through recovery and beyond.