Ca 19-9 Blood Test and Relationship with Pancreatic Cancer
About the Ca 19-9 Blood Test
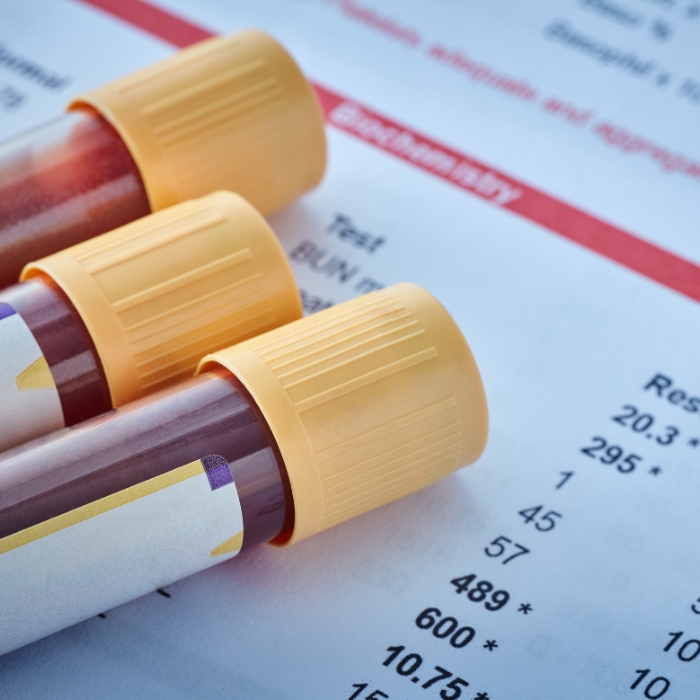
The Ca 19-9 blood test, also referred to as carbohydrate antigen 19-9, is a type of blood test conducted to measure the levels of a protein called CA 19-9 found in the blood. This type of protein results from pancreatic cells as well as other cells within the body, such as those of the gallbladder and liver.
The Ca 19-9 test is very much used as a tumor marker in order to detect cancers such as pancreatic cancer. The increased level of CA 19-9 in the blood may indicate the presence of pancreatic cancer; however, it may also be raised in several other benign disorders such as obstructive jaundice, pancreatitis, and liver disease.
Role of Ca 19-9 Test in Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
The blood test for Ca 19-9 has an important place in diagnosis and management regarding pancreatic cancer. As this is not a screening test of pancreatic cancer in the general population, it is usually ordered in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies, which help diagnose pancreatic cancer.
If the levels of CA 19-9 are high in a patient who has been suspected to suffer from cancer of the pancreas, then that may point out that the pancreas has a tumor. However, increased levels of CA 19-9 may also occur even in non-cancerous disorders, which may bring a need for further testing to be done for the confirmation of the diagnosis.
Monitoring Treatment of Cancer of the Pancreas
The Ca 19-9 blood test is among the diagnostic methods utilized to monitor the course of treatment in patients with pancreatic cancer. Sometimes CA 19-9 will be measured after treatment has ended to monitor the success of the therapy and to detect signs of cancer recurrence.
Changes in CA 19-9 over time can provide doctors with further details on how well the treatment is going and if more interventions are necessary. On the other hand, results of CA 19-9 need to be interpreted in relation to other clinical findings and imaging studies.